Bone Over The Line Types
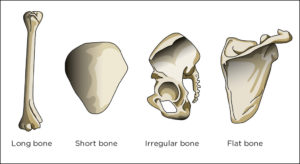
The bones of the human body are made up of several bone over the line types, or subtypes. Each type of bone has its own specific anatomical features, including its length, shape, and mineral content. The three main categories are tibia, femur, and scapula. A detailed description of the various types of bone can be found in the following sections. Listed below are the main subtypes and their differences.
oSpongy Bone – These bones contain irregular cavities that are more dense than compact bones. These cavities are connected to one another via a network of canaliculi, which receive blood supply from the adjacent cavities. Trabeculae – These tiny plates of bone tissue form an orderly pattern and provide the bone with maximum strength. As a result, spongy bones are lighter than compact bones.
oCement Lines – These lines are found in all types of bone, including osteons. They show that new bone is being deposited on top of an old surface. This feature is not uncommon. It is an important sign of a healthy body. But there are certain factors that determine the appearance of a bone over the line. A cement line indicates that it is not an indication that the bone is dead.
oOsteoclasts – These cells are present in all types of bone. They are large, cylindrical cells that come from the bone marrow. They are related to white blood cells and have multiple nuclei. They are found on the surface of the mineral in the bone. They help the body in many ways, including providing structural support. If you’re experiencing fractures or degenerative diseases, these can be a sign that you’ve lost a part of your body.
The main difference between bone types is that one type contains type I collagen. The other type contains type II collagen. The line of cement in the bone is the same as the line of cement on an uncemented surface. In this case, this means that the bone is not uncemented bone. Instead, it contains the same minerals that create it. This is good because it means it’s not crumbly.
The two types of bones are spongy and hard. The former is more flexible, but is still a solid structure. As a result bone tissue can have different shapes and sizes. For example, long bones are longer than wide ones and can have a lot of cancellous bone at their ends. Conversely, short bones are roughly cubic in shape and consist of a narrow, spongy nucleus under dense, compact bone.
The cortical layer of bone is made up of two types of collagen. Its cortex is smooth and continuous, and type II collagen is composed of protein-rich cells and fibroblasts. This structure provides strength. The femur is a tubular structure with a continuous cavity in the center. The outer layer of the cortex is called the periosteum. This is a two layer structure.
All bones have a cortex, which is the outer layer of the bone. It is continuous, smooth and has a variable thickness. The skeleton is made up of layers of bone called trabeculae. Trabeculae enclose spaces containing blood vessels and bone marrow. This structure allows bones to be distinguished by line types. In addition, it provides a continuous bone block and cross internal struts.
Type I collagen is 90% organic matrix. The rest of the bone is made up of other proteins and proteoglycans. However, type I collagen is the most abundant type of bone in the human body. Its composition varies depending on the bone, the type of line, and the type of collagen used in bone formation. The other two types of bone are spongy and cortical. They differ in their characteristics and their properties. You can find more information about the structure of bones and their treatment on the website https://antisantikuman.com/.
Unlike other bone types, the compact and tibia are very common. During development, these cells are able to develop into different cell types. For example, osteoblasts develop into osteocytes, cells found on the surface of a bone. As they age, they die due to a process called apoptosis. This cell type is trapped within the skeletal structure, where it controls how much stress is placed on the bones.
