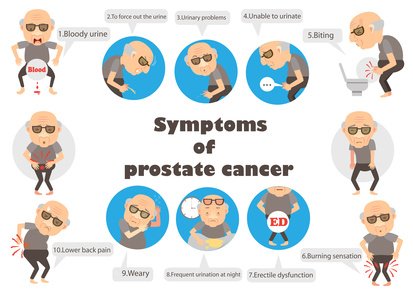
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is actually a type of malignant neoplasm, which grows in the prostate gland
It is the most common cause of death for men in America. It has the highest mortality rate of any cancer among men, and it has been estimated that about 1 in every 8 men will develop prostate cancer in his life. This year alone, over 192,000 men are expected to be diagnosed with this form of cancer.
The symptoms of this cancer vary from person to person and may also differ by stage of the cancer. But in general, symptoms are similar to those of other cancers, particularly those of the kidney or bones. When symptoms begin to show, a physician should not wait. It is crucial to have a thorough examination done by a physician to determine the nature of the cancer, so that he can properly diagnose it.
A variety of different signs can indicate that a man has prostate disease, including a change in sexual desire, urinary frequency, difficulty or pain in urination, pain while urinating, and feeling bloated. In some men, the prostate may even feel swollen during urination. If there is no change in any of these signs, it may be safe to assume that there is no prostate disease present. However, if any of these signs occur, it is crucial to consult a physician.
Prostate disease is caused by a tumor that can grow in the lining of the prostate, causing it to become enlarged and inflamed. There are a variety of different tumors that can grow in the prostate. These types include: adenocarcinoma, pSA Prostate Specific Antigen -positive, and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
If a man has a PSA (Prostate Specific Antigen) -positive test, he should see a physician as soon as possible. This test shows that the blood contains a particular kind of hormone known as PSA. The hormone PSA indicates the amount of PSA in a man's blood. When a man has an increased amount of this hormone, it suggests that he may have an elevated PSA level.
The next sign that a man should check is whether there is any evidence of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. in his urine
This is not a serious problem, but it is something to be concerned about. A condition called prostatitis occurs when a man's prostate becomes infected with a bacterium called Prostatococcus that causes inflammation of the urethra and its lining. Infection of the urethra with Prostatococcus can lead to a urinary tract infection, as well as to cancer of the bladder. It is important for a man to have a complete physical exam and to discuss the matter with his doctor before this condition becomes severe.
A pelvic exam is also helpful in detecting the early stages of prostate cancer. A medical examination can tell a doctor whether a man is experiencing any problems with the prostate such as blood in the urine, pain in the lower back, or whether there is swelling in the groin area. Some symptoms that might indicate prostate cancer include a change in the size of the testicles, a receding hairline, pain in the scrotum or the perineum, pain in the scrotum or buttocks, and swelling of the testicles.
Another way that doctors can detect prostate cancer is to look for fluid in the urine, whether it is urine or blood, or if it has been formed in the urethra. This may be a sign of a problem with the urethra, such as a blocked urethra, scarring or blood in the urine, or a blockage in the urethra.
If a man notices that there is blood in the urine, he should contact a doctor right away to determine whether it is due to a urinary tract infection or a urinary bladder disorder. These two conditions are often confused, but they are two separate conditions.
There are many more prostate cancer symptoms that can be very scary. Knowing what to look for and how to diagnose a man's prostate cancer can save his life. By keeping an eye on these symptoms, it is easy for a doctor to keep a patient healthy and free of prostate cancer.
